Search Results
Results for: 'nephron tubules'
Antidiuretic hormone (vasoconstriction, water reabsorption & sweat inhibition)
By: HWC, Views: 6590
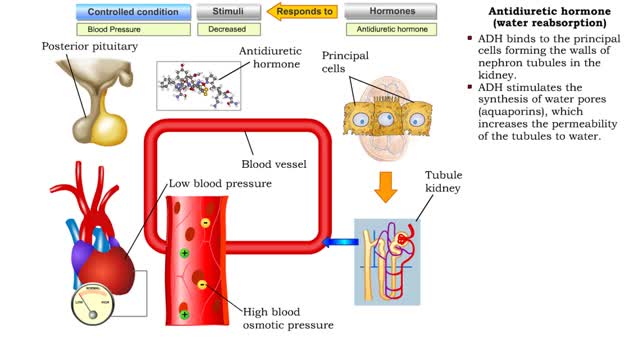
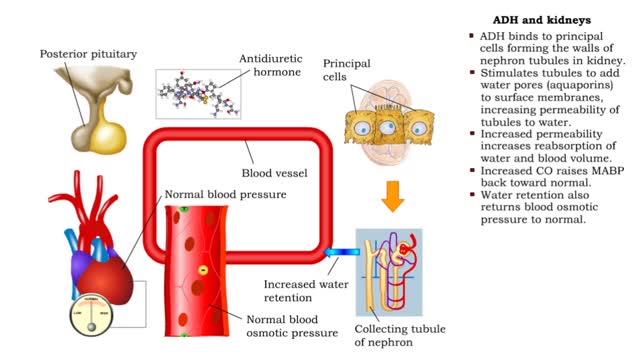
• Dehydration, blood loss, and low amounts of water in the blood can cause blood volume and pressure to decrease. • Neurosecretoxy cells in the posterior pituitary release antidiuretic hormone(ADH). • ADH binds to smooth muscle cells in blood vessel walls, stimulating them to vasoconstr...
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 6781
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
By: HWC, Views: 7360
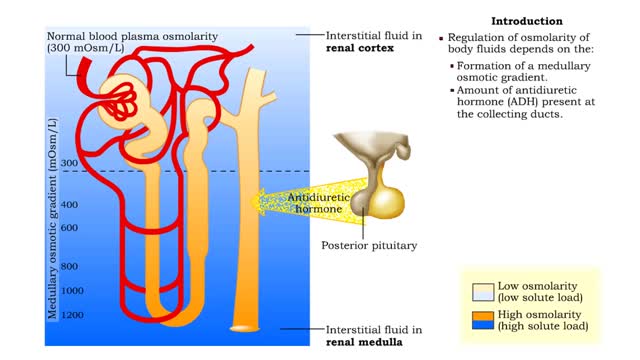
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 6545
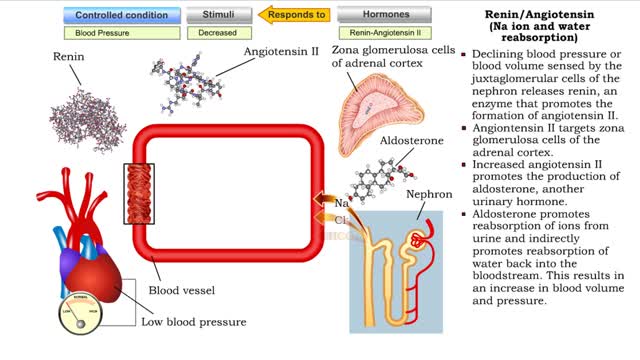
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 6999
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
By: HWC, Views: 4595
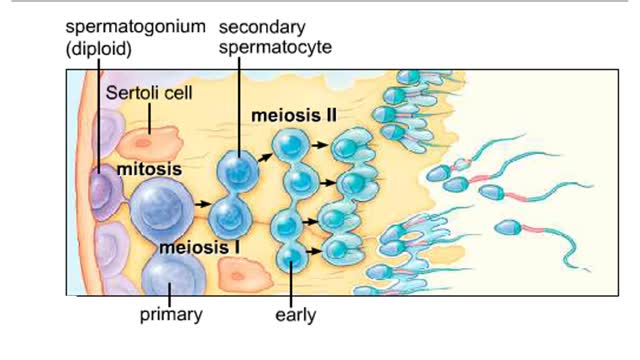
Spermatogenesis takes place inside the seminiferous tubules. Diploid spermatogonia located near the outer edge of the tubule divide mitotically to form primary spermatocytes. The first meiotic division produces secondary spermatocytes with a haploid number of duplicated chromosomes. T...
Introduction to filtration - filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 6799
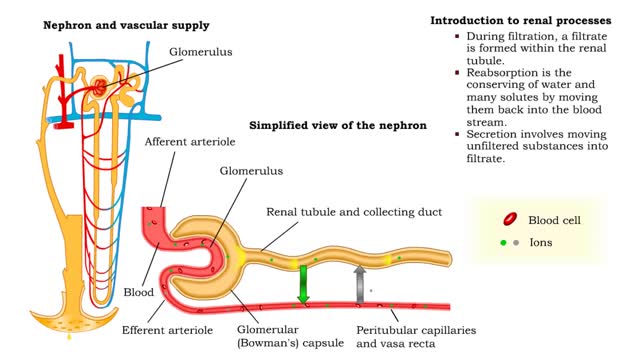
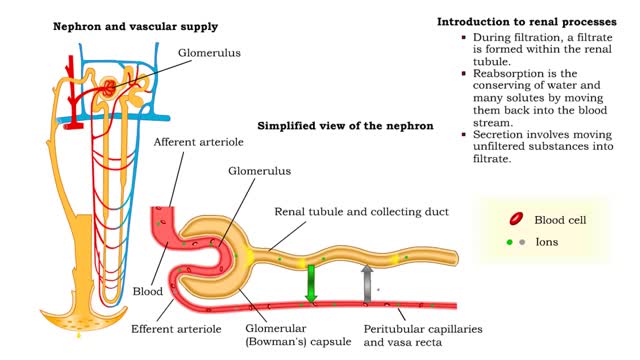
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 7102
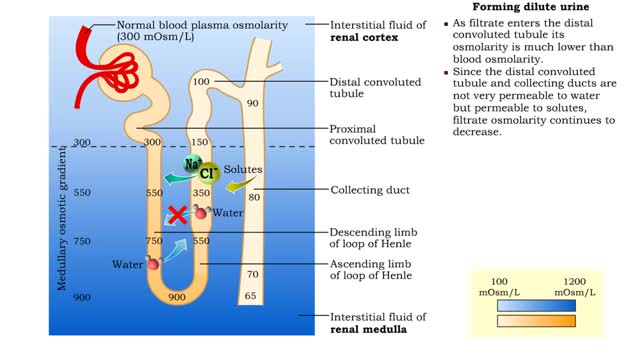
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Introduction to renal processes and filtrate formation and composition
By: HWC, Views: 6900
• At the nephron, the three process responsible for the formation of urine include: • Glomerular filtration. • Tubular reabsorption. • Tubular secretion. • During filtration, a filtrate is formed within the renal tubule. • Reabsorption is the conserving of water and many s...
Advertisement